Dye Penetrant Inspection
Dye Penetrant Testing, also known as Dye Penetrant Inspection, Liquid Penetrant Inspection, Penetrant Testing or Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection, is a method of non-destructive testing that is used to reveal any surface breaking flaws in all non-porous materials, regardless of size, such as metals, plastics and ceramics. Dye Penetrant Testing can also be applied to both ferrous and non-ferrous materials.
The Benefits Of Dye Penetrant Testing
What Dye Penetrant Testing Is Used For
This NDT process is often used to detect defects in forged, welded or cast components that suffer from a greater risk of surface flaws, such as cracking. Dye Penetrant weld inspection is a common service for our NDT team. SlimDril works with a wide range of industry sectors including Aerospace,Automotive, Energy & Gas, Construction and Engineering and we are able to provide Dye Penetration Testing both on-site or at our testing facility,
Dye Penetrant Testing is also popular as it is extremely portable. making it highly convenient when testing on-site or for inspecting surface discontinuities.
Dye Penetrant Testing is also popular as it is extremely portable. making it highly convenient when testing on-site or for inspecting surface discontinuities.
How Dye Penetrant Testing Works
The Dye Penetrant Testing process is based on the ability of a liquid to be drawn into a surface-breaking flaw by capillary action.
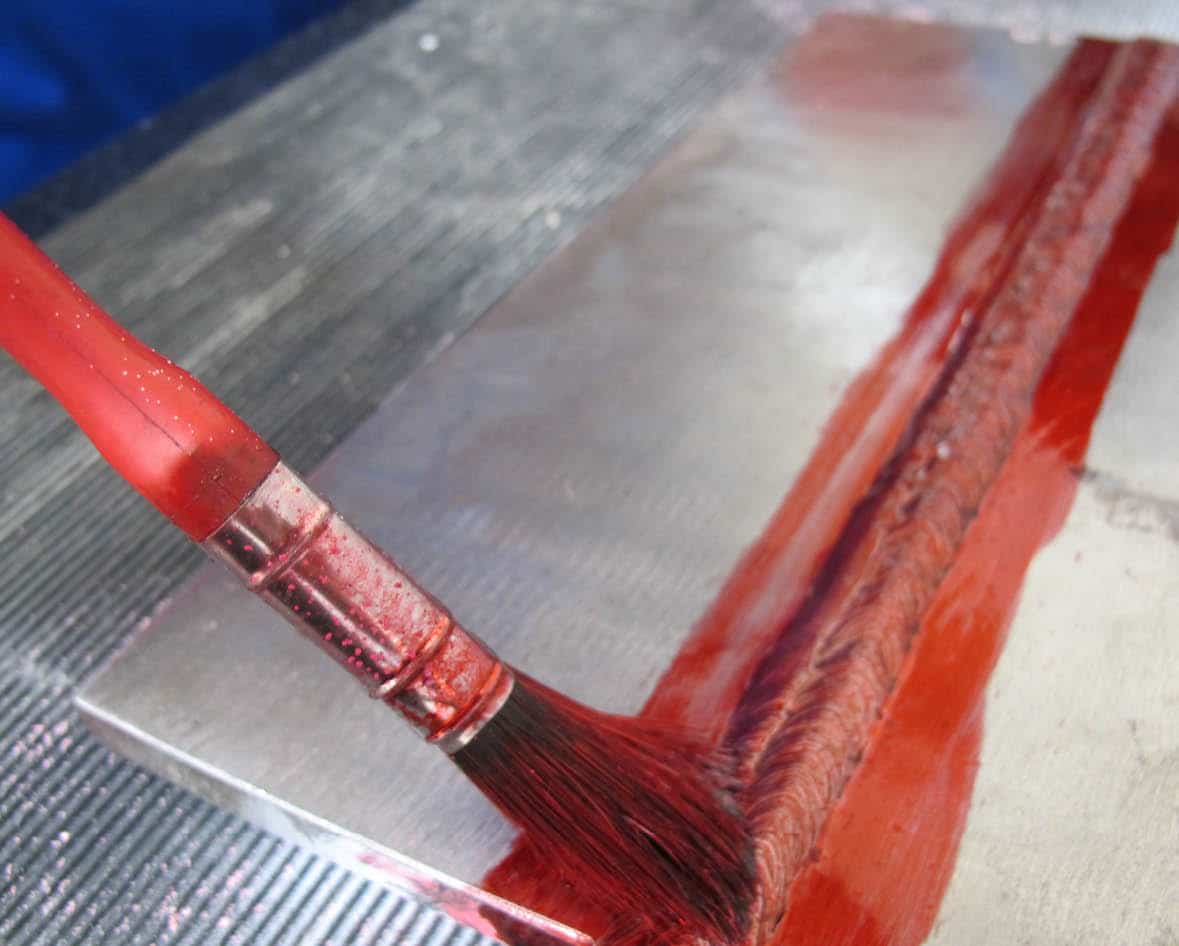
The first step is to clean the component that is being tested before applying the penetrant. Then a visible or fluorescent dye that is either water or solvent-based is then applied to the surface of the component by a variety of applications including spraying, brushing, dipping or full immersion of the component into the penetrant dye.
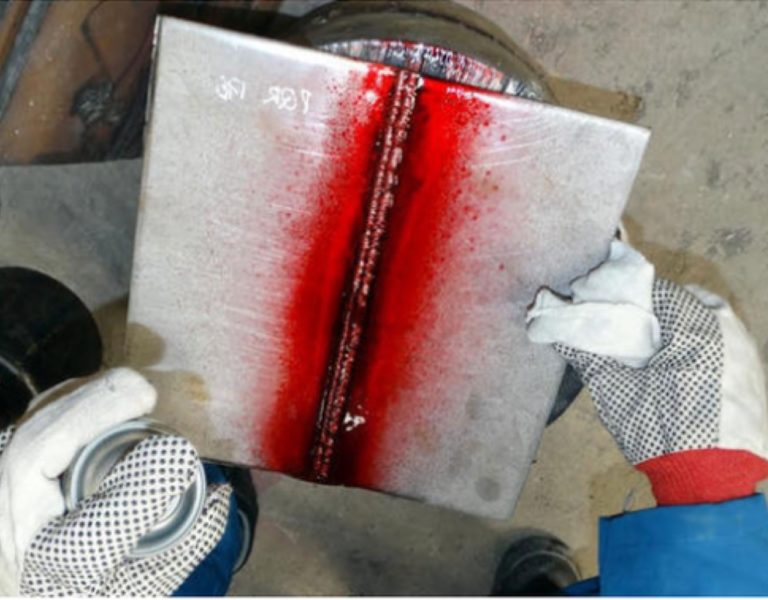
During the penetration time, or dwell time, the coloured dye penetrates any surface breaking flaws that might exist in the component through capillary action. The length of the penetration time depends on the dye or penetrant that is being used. Any excess penetrant is then removed from the surface of the tested component before it is dried. A developing agent is then applied. The developing agent draws the penetrant out of any surface breaking flaws and onto the surface in a reverse process of capillary action. This forms a visible indication that reveals any flaws in the component ready for a visual inspection and reporting.
Our inspectors then perform a visual inspection using either white light or ultraviolet light depending on the type of penetrant that was used. (White light for colour contrast penetrant and ultraviolet light for fluorescent dyes.)
The first step is to clean the component that is being tested before applying the penetrant. Then a visible or fluorescent dye that is either water or solvent-based is then applied to the surface of the component by a variety of applications including spraying, brushing, dipping or full immersion of the component into the penetrant dye.
During the penetration time, or dwell time, the coloured dye penetrates any surface breaking flaws that might exist in the component through capillary action. The length of the penetration time depends on the dye or penetrant that is being used. Any excess penetrant is then removed from the surface of the tested component before it is dried. A developing agent is then applied. The developing agent draws the penetrant out of any surface breaking flaws and onto the surface in a reverse process of capillary action. This forms a visible indication that reveals any flaws in the component ready for a visual inspection and reporting.
Our inspectors then perform a visual inspection using either white light or ultraviolet light depending on the type of penetrant that was used. (White light for colour contrast penetrant and ultraviolet light for fluorescent dyes.)
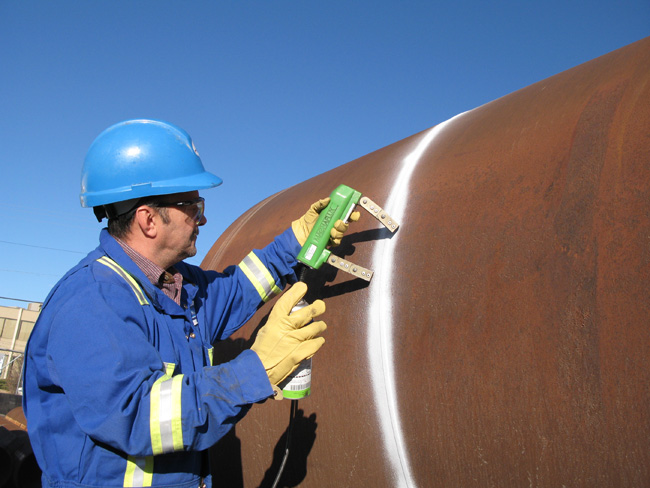
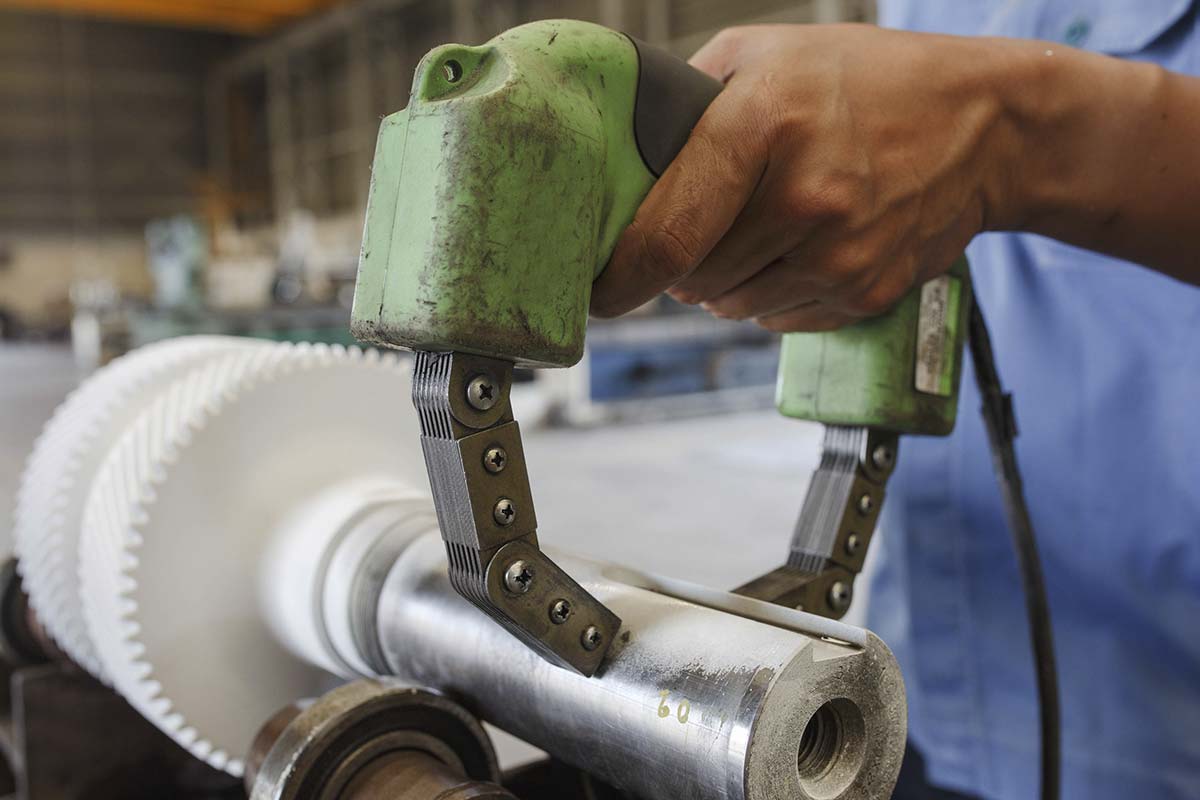
Magnetic Particle Testing
Magnetic Particle Inspection, also known as Crack Testing or Magnetic Particle Testing, is a method of non-destructive testing that can be used to find any surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials such as steel and iron. Magnetic Particle Inspection is a quick and relatively easy NDT technique and is widely used in all industry sectors including Aerospace, Power Generation, Automotive and Construction.
The Benefits Of Magnetic Particle Inspection
What Magnetic Particle Inspection Is Used For
Magnetic Particle Inspection is used to detect surface or near-surface flaws such as cracks, laps, seams and inclusions in ferromagnetic materials such as steel and iron. One of Magnetic Particle Testing’s main advantages is that it immediately identifies any surface or near-surface defects in ferromagnetic components.
Magnetic Particle Testing can be used on a variety of components and equipment such as engine parts, suspension and braking components, castings, forgings and weldments.
Magnetic Particle Testing can be used on a variety of components and equipment such as engine parts, suspension and braking components, castings, forgings and weldments.
How Magnetic Particle Inspection Works
During the process of Magnetic Particle Inspection, the specimen is magnetised either locally or overall depending on the size of the specimen and a magnetic field is induced in the component. The testing process analyses the magnetic flux around the tested component.
If the tested material is sound, then the magnetic flux will predominantly remain inside the material. However, if there is a surface-breaking flaw during the Magnetic Particle Inspection then the magnetic field will be distorted, causing local magnetic flux leakage around the flaw on the surface.
If the tested material is sound, then the magnetic flux will predominantly remain inside the material. However, if there is a surface-breaking flaw during the Magnetic Particle Inspection then the magnetic field will be distorted, causing local magnetic flux leakage around the flaw on the surface.
This leakage can be detected by dusting the surface of the specimen with fine magnetic particles such as ferrous iron filings. The particles will then be attracted to the area of the flux leakage, creating a visible indication of the defect.
The indication is then noted and evaluated by the operator to determine what might have caused the flaw and suggest action to take. There are two methods of Magnetic Particle Inspection. The first is white colour contrast, which is ideal for daylight and site work. the other makes use of Ultra Violet light. Here at SlimDril, we provide both an ultraviolet method as well as the black and white contrast method.